Microcystis cause freshwater cyanobacteria blooms that effect drinking water, water-based recreation, and ecology.
 |
| https://www.usgs.gov/media/images/microcystis-aeruginosa-bloom-0 |
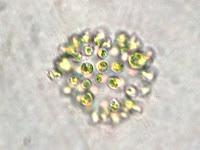 |
| Light microscopy image from Wikipedia |
 |
| Microcystis wesenbergii colony under epifluorescence microscopy with SYTOX Green DNA staining. Image from Wikipedia. |
Microcystis produce microcystin.
Microcystin is a nonribosomally synthesized cyclic hepatotoxin (liver toxin) with potent inhibitory activity against mammalian protein phosphatases.
Recently, the TaqMan PCR, or the Taq nuclease assay (TNA), was introduced to quantify specific genotypes of picocyanobacteria (Becker et al., 2000) or microcystin-producing cyanobacteria in the field (Foulds et al., 2002).
TNA utilizes a sequence specific dually labeled fluorescent probe (TaqMan probe) and primers to quantify the level of DNA template initially present in a sample.
The rate of exponential accumulation of the amplicon is monitored by the hydrolysis of the TaqMan probe, in which it generates a fluorescent signal during the amplification process.
The threshold cycle (Ct) is the PCR cycle number at which the fluorescence passes a set threshold level and can be used to determine the starting DNA amount in the sample based on a standard curve (based on samples with a known concentration).
For Kurmayer and Kutzenberger (2003), cell numbers inferred from TNA standard curve correlated significantly with the microscopically determined (particle counting) cell numbers on a logarithmic scale.
They conclude that the Microcystis cell numbers could be used to infer the mean proportion of mcy genotypes in Lake Wannsee (Berlin, Germany). I could use these methods to study mcy genotypes in Bellingham Bay. Kurmayer and Kutzenberger (2003) do not mention issues with multiple copy numbers or cross-reactivity.
Proposed experiments to study Microscystis:
Culture several unicellular strains of Microcystis sp. to test primer and TaqMan probe sensitivity and specificity. TaqMan PCR, or the Taq nuclease assay (TNA) will be used to quantify the mcyB region. The TaqMan probes are from Kurmayer and Kutzenberger (2003; 5' - CACCAAAGAAACACCCGAATCTGAGAGG-3) The probe will have a fluorescent reporter dye (6-carboxyfluorescein) covalently attached to the 5' end (5' -FAM) and a 3' -TAMRA fluorescent quencher
dye (6-carboxytetramethylrhodamine). A standard curve based on predetermined cell concentrations will be established by relating the known DNA concentrations (in cell equivalents) to the Ct of the diluted samples.
References:
Becker et al., (2000) PCR Bias in Ecological Analysis: a Case Study for Quantitative Taq Nuclease Assays in Analyses of Microbial Communities
Foulds et al., (2002) Quantification of microcystin-producing cyanobacteria and E. coli in water by 5 -nuclease PCR
Kurmayer and Kutzenberger (2003) Application of Real-Time PCR for Quantification of Microcystin Genotypes in a Population of the Toxic Cyanobacterium Microcystis sp.

No comments:
Post a Comment